Unlocking the Secrets of the Lean Startup Movement (2024 Edition)
This comprehensive guide explores how Lean Startup principles serve as a blueprint for success for companies both new and established looking to adapt quickly, unlock growth and delight customers.

The winds of change are sweeping through the business world faster than ever before. Companies must embrace agility, innovation and constant learning to stay ahead. Enter the Lean Startup movement - a methodology that has taken the entrepreneurial world by storm over the past decade.
Staying ahead of the competition is of utmost importance. The Lean Startup methodology has emerged as a powerful approach that promotes innovation, agility, and growth for both new ventures and established companies. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the key principles, success stories, and resources available to help entrepreneurs and business leaders harness the power of Lean Startup to propel their businesses forward.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how Lean Startup principles can serve as a blueprint for success for companies both nascent and established. You will discover real-world examples of startups that rapidly grew into household names by following Lean thinking. Additionally, you will learn which tools and techniques enable startups to systematically test assumptions and make data-driven decisions.
Whether you are a startup founder ready to disrupt an industry or a corporate executive aiming to spur innovation within your organization, this guide will arm you with the knowledge to unleash the power of Lean Startup. With these principles in your toolkit, you will be able to adapt faster, unlock growth and delight customers in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Lean Startup method emphasizes rapid iteration, testing hypotheses, and incorporating user feedback. This builds capital-efficient and innovative products.
- Successful startups like Dropbox, Airbnb, Instagram, and Zappos designed phenomenal products by strongly adhering to Lean principles.
- Powerful frameworks like the Business Model Canvas help startups systematically test assumptions by tracking actionable metrics. This leads to data-backed decisions.
Embracing the Lean Startup Methodology
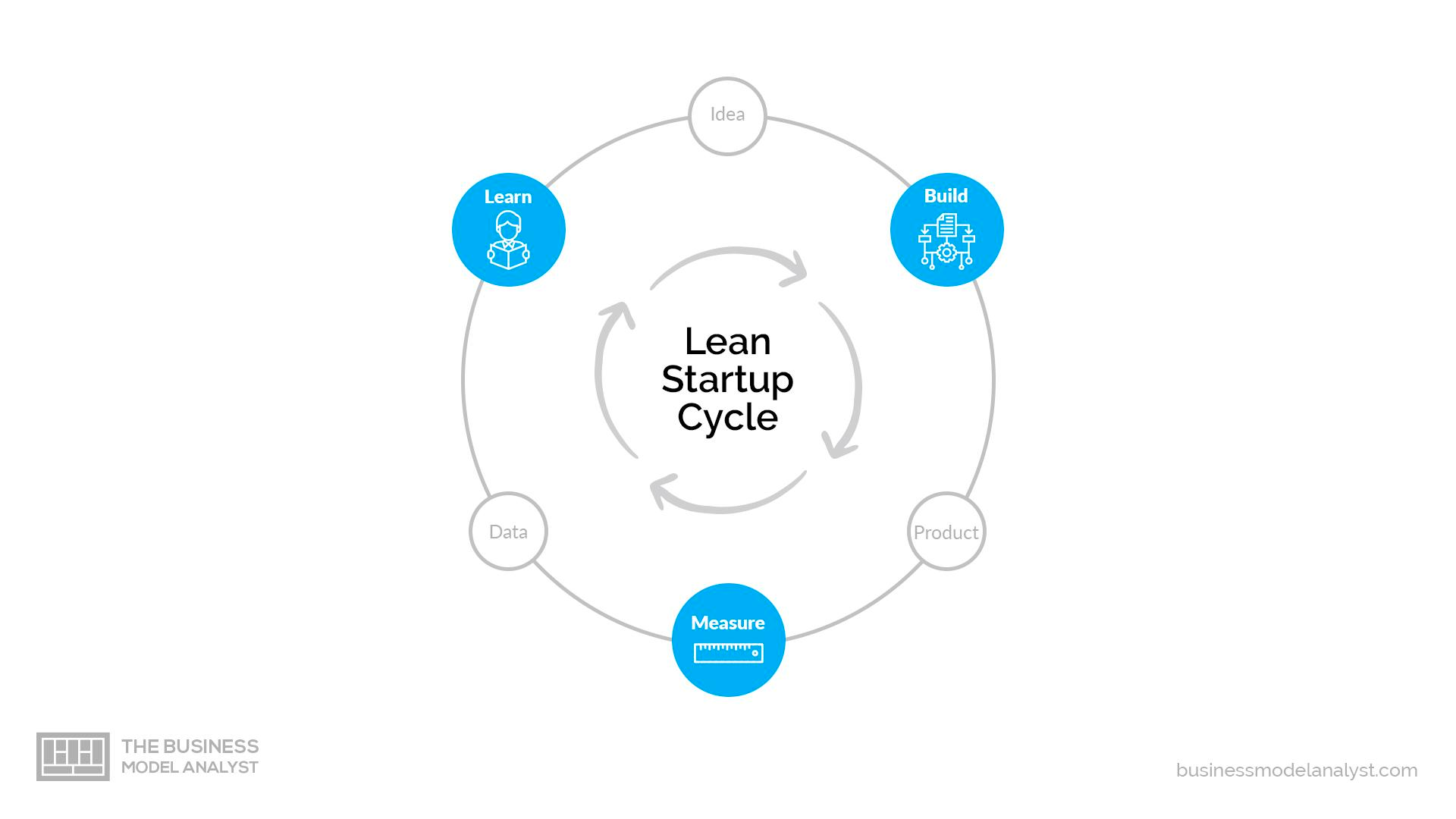
The Lean Startup methodology revolves around waste reduction, value maximization, and the incorporation of customer feedback to craft products that cater to particular needs. Since its introduction by Eric Ries in 2008, the methodology has gained significant attention and has been widely adopted by successful entrepreneurial businesses. At its core, the Lean Startup methodology is based on two essential principles: customer feedback is paramount, and continuous feedback yields the best outcomes.
Understanding customers' needs and satisfying them with minimal resources – known as customer development – ultimately leading to a sustainable business model, is the focus of the Lean Startup approach. To ensure their continued success and development, corporations must continually create innovative business models, a concept that has been featured in publications like the Harvard Business Review. The Lean Startup methodology has proven to be a valuable tool in managing successful startups and driving innovation in various industries.
Origins and Evolution
The Lean Startup movement is rooted in lean manufacturing and customer development techniques, with a focus on learning and improvement. The customer development methodology, created by Steve Blank, emphasizes learning about customers and their needs as soon as possible in the development process. Another related concept is discovery-driven planning, which encourages an entrepreneurial mindset to planning and has inspired the Lean Startup methodology.
Today, the Lean Startup ecosystem is thriving, with meetups in more than 100 cities and 17 countries. Examples of companies that have successfully applied the Lean Startup approach include Dropbox, Zappos, and General Electric, demonstrating the success of this methodology across multiple industries.
As the Lean Startup movement continues to evolve, entrepreneurs and business leaders, including those from Harvard Business School, can learn from these success stories and apply the principles to their own more successful entrepreneurial business ventures.
Key Principles
Minimum viable product (MVP), continuous deployment, split testing, actionable metrics, pivoting, and innovation accounting are among the key concepts of the Lean Startup. The MVP is a version of a new product that allows a team to gain the greatest insights about customers with the least effort. This idea allows startups to:
- Test their assumptions
- Gather customer feedback
- Learn from the market
- Avoid investing heavily in product development
Continuous deployment involves instantly deploying all code written for an application into production, while split testing is a type of experiment where different versions of a product are simultaneously offered to customers. By incorporating these key principles, businesses can become more successful entrepreneurial ventures by quickly adapting to customer needs and market changes.
Delivering a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) using Lean Startup Principles
A minimum viable product (MVP) is a crucial concept in the Lean Startup methodology. It is a prototype version of a product that allows startups to validate their assumptions and get user feedback with minimal time and effort invested.
An MVP has just enough features to satisfy early customers and provide actionable insights for future product development. It should be the simplest possible product that lets you start learning from customers.
Key characteristics of an MVP:
- Focuses on core features that deliver maximum customer value
- Avoids unnecessary bells and whistles
- Easy and fast to build
- Flexible to change based on feedback
- Enables data collection about customer usage
Follow these key principles when developing an MVP:
- Identify the Riskiest Parts of Your Idea
Determine which core assumptions about your product and customers are most risky. An MVP should focus on testing those riskiest assumptions first. - Focus on Core Features
Include only essential features that allow you to test the riskiest assumptions. Avoid adding too many bells and whistles. - Simplify the User Experience
Streamline the user interface to make it extremely easy for testing users to accomplish key tasks. - Engage Early Adopters
Test your MVP with a small group of target customers who are likely to be early adopters. Their feedback is invaluable. - Measure and Learn
Use analytics tools to understand how test customers are using the MVP. Gather feedback through surveys and interviews. - Iterate Quickly
Be prepared to modify the MVP based on insights gained. Short iteration cycles allow faster product refinement. - Define Success Metrics
Identify key metrics that determine if your MVP hypotheses are correct. Use those to decide if you should pivot or proceed.
By following these principles, startups can build an MVP that serves as an efficient, low-cost experiment to validate their ideas with real-world data. This ultimately helps create products that effectively meet customer needs.
Success Stories: Lean Startups in Action
Notable Lean Startup success stories include companies like:
- Dropbox
- Zappos
- Buffer
- Wealthfront
- Groupon
These companies have demonstrated the effectiveness of the Lean Startup methodology in various industries, showcasing the versatility and adaptability of the approach.
By learning from these success stories, entrepreneurs and business leaders can apply the Lean Startup principles in their own ventures and achieve similar success. Each of these companies has employed the lean startup process in their own unique ways, adapting and iterating based on customer feedback and market conditions.
The subsequent sections will delve into the utilization of the Lean Startup approach by each of these companies, leading to their remarkable growth and success within their respective industries.
Dropbox
Dropbox is a remarkable success story, marked by its impressive growth and revenue generation. Here are some key facts about Dropbox.
It all began like this...
- Over 50 million users
- Projected annual revenue of $240 million
- The company’s journey began when founder Drew Houston needed a USB flash drive while studying at MIT
- Dropbox employed the Lean Startup approach to test and validate its file-sharing service before expanding its reach
This approach allowed Dropbox to rapidly grow its user base and revenue, ultimately leading to the company going public in 2018 with a valuation of $8 billion. Dropbox’s adherence to the Lean Startup methodology enabled it to create a product that fulfilled its customers’ needs, propelling its success in the competitive file hosting service industry.
Zappos
Zappos, the online shoe retailer, offers another prime example of Lean Startup success. The company tested its hypothesis by approaching local stores, taking photos of their products, and listing them for sale on their website. This hands-on approach allowed Zappos to validate the market demand for an online shoe retailer.
Zappos, applying Lean Startup principles, was able to promptly ascertain customer demand for their product, paving the way for a successful online retail business. Today, Zappos is a well-known brand and continues to be a leader in the online shoe retail space.
Buffer
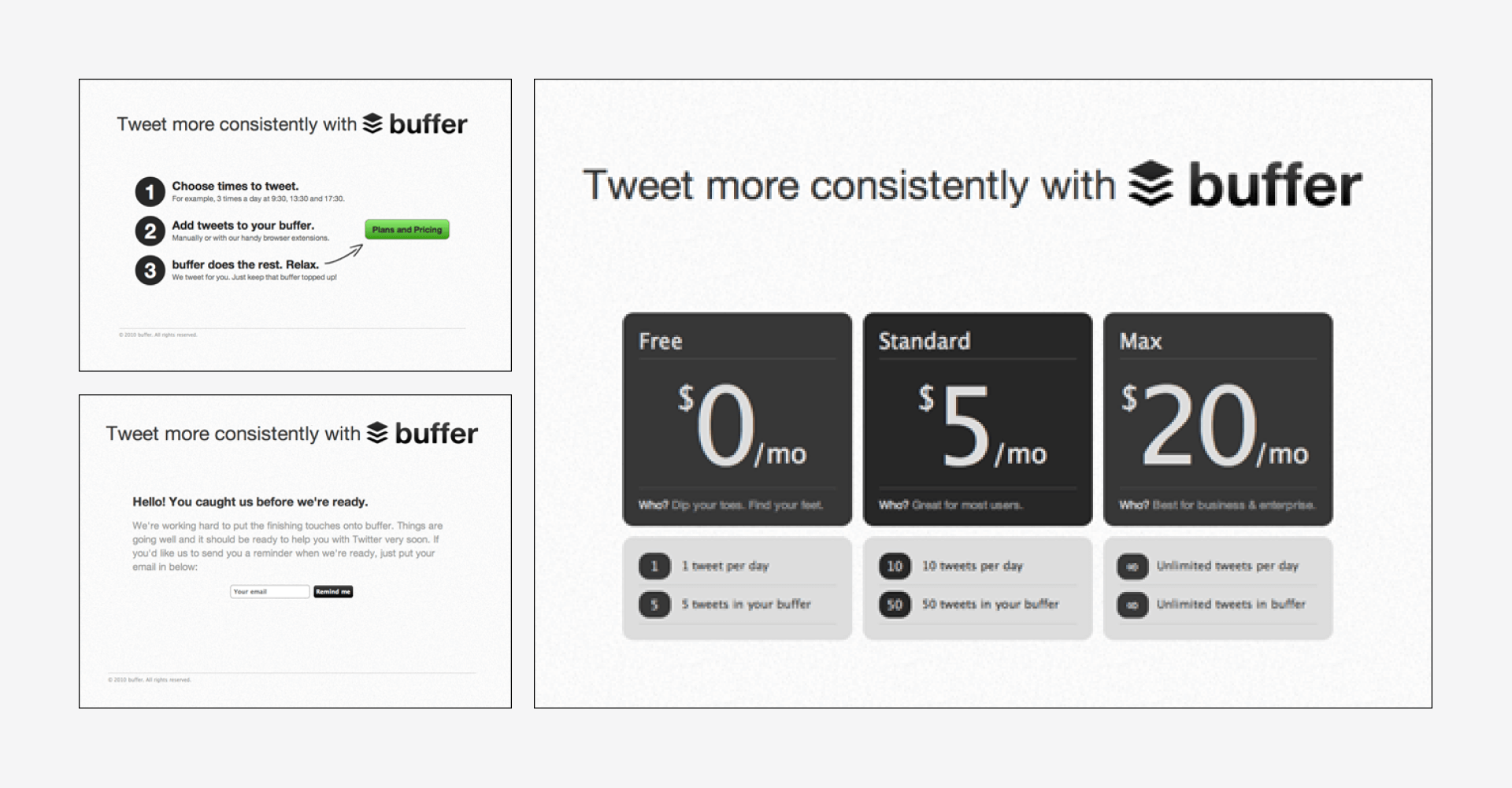
Buffer, a social media management platform, has seen tremendous success since its founding in 2010. It has grown from $0 to an impressive $20 million in annual recurring revenue within 9 years. The co-founders, Joel Gascoigne and Leo Widrich, set out with the goal of creating a tool to help people manage their social media accounts more efficiently. To validate their idea, they created a landing page to gauge interest before fully developing the product.
Buffer’s success can be attributed to:
- Its dedication to transparency, both internally and externally
- Its commitment to providing value to its customers
- Its use of the Lean Startup methodology, which allowed it to collect customer feedback and iterate based on this feedback
- Its product that catered to its users’ needs
Today, Buffer is a popular social media management tool with a loyal customer base.
Twitter, the popular microblogging platform, began as a podcasting platform called Odeo. However, the founders quickly realized that their initial idea was not gaining traction and decided to pivot using Lean Startup principles. They shifted their focus from podcasting to microblogging, a decision that ultimately led to Twitter’s massive success.
Today, Twitter has over 500 million registered users and is one of the most popular social networking sites in the world. Twitter’s founders’ adoption of the Lean Startup methodology enabled them to modify their original concept, resulting in a platform that struck a chord with users and became a worldwide phenomenon.
Instagram, the popular photo-sharing platform, initially started as a location-based app called Burbn. However, the founders quickly realized that their original idea was not gaining traction and decided to pivot using the Lean Startup approach. They shifted their focus from location-based services to photo-sharing, a decision that ultimately led to Instagram’s rapid growth and success.
Today, Instagram has over a billion users and is one of the most popular social media platforms in the world. Instagram’s founders, by leveraging the Lean Startup methodology, were able to refine their original concept into a platform that truly resonated with users, thereby becoming a global phenomenon.
Wealthfront
Wealthfront, an automated investment service, has managed to apply Lean Startup principles to develop its platform, which now manages over $4.6 billion in assets from nearly 100,000 users. Founded in 2008 by Andy Rachleff, Wealthfront has continually developed its product offerings to meet the needs of its ever-growing clientele.
Wealthfront, by implementing the Lean Startup methodology, was able to develop an investment service that catered to its users’ needs, facilitating remarkable growth in a highly competitive industry. Today, Wealthfront is one of the leading robo-advisors in the industry, managing billions of dollars in assets for its clients.
Groupon
Groupon, known for its online coupon promotions, began as an activism platform called The Point. However, the founders quickly realized that their initial idea was not gaining traction and decided to pivot using Lean Startup methods. They shifted their focus from activism to online coupon promotions, a decision that ultimately led to Groupon’s rapid growth and success.
Today, Groupon is a well-known brand and continues to be a leader in the online coupon promotion space. Groupon’s founders, through their adoption of the Lean Startup methodology, were able to alter their initial concept, creating a platform that resonated with users, thereby achieving remarkable success in the competitive market.
Adapting Lean Startup for Established Companies
Established companies can also benefit from implementing lean start up practices, as it can drive innovation and help them stay competitive in the market. By applying the Lean Startup methodology, these companies can foster a culture of experimentation, customer-centricity, and continuous learning, which can lead to improved products and services and ultimately, better business outcomes.
Even though large companies operate on a different scale, they can still benefit from startup lessons. For instance, they can adopt lean methodologies to foster innovation and efficiency within their organizations. They can also embrace the startup culture of agility and adaptability to stay competitive in rapidly changing markets. Applying lean will fundamentally change how large companies operate and deliver results – including traditional businesses applying lean manufacturing to their operations.
In the subsequent sections, we'll delve into the following topics:
- Implementation of Lean Startup practices for established companies
- The Lean Enterprise approach
- Potential challenges that may arise during this process.
Implementing Lean Startup Practices
For established companies embarking on the implementation of Lean Startup practices, fostering a culture that values experimentation, customer-centricity, and continuous learning is crucial. This involves:
- Utilizing the Build-Measure-Learn cycle
- Introducing the concept of Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
- Focusing on validated learning
- Tracking progress through innovation accounting.
Adopting these practices can help established companies cultivate an environment conducive to innovation and continuous improvement. This can lead to more agile and adaptive organizations, which are better equipped to respond to changing market conditions and customer needs.
Lean Enterprise

The Lean Enterprise approach combines Lean Startup principles with other methodologies to facilitate innovation in larger organizations. This approach is all about:
- Providing value to the customer with as little waste and processes as possible
- Emphasizing ongoing improvement
- Understanding customer needs
- Streamlining processes along the value chain.
Established companies can benefit from embracing the Lean Enterprise approach in the following ways:
- Boost efficiency
- Enhance customer satisfaction
- Cut costs
- Rapidly identify and tackle issues
- Swiftly adjust to ever-changing market conditions
Overcoming Challenges
When implementing Lean Startup practices in established companies, some challenges may arise, such as dispersed ownership of the customer, lack of clear business ownership and commitment, and adjusting to various contexts and industries. To address these challenges, companies must be willing to undergo changes, cultivate a culture of ongoing improvement, and have a good understanding of customer requirements.
Furthermore, it’s important for companies to allocate resources effectively and consider restructuring their organization to better support Lean Startup practices. By addressing these challenges, established companies can successfully implement Lean Startup practices and drive innovation in their organizations.
The Lean Startup Ecosystem

The Lean Startup ecosystem is a vibrant community that consists of conferences, meetups, and educational programs that support the methodology and bring together practitioners. By participating in these events and programs, entrepreneurs and business leaders can gain valuable insights, network with like-minded individuals, and learn from the experiences of others who have successfully implemented the Lean Startup approach.
In this section, we’ll delve into the myriad resources within the Lean Startup ecosystem. This includes conferences, meetups, and educational programs designed to help entrepreneurs and business leaders comprehend and apply the Lean Startup methodology.
Lean Startup Conferences and Meetups
Lean Startup conferences and meetups provide opportunities for networking, learning, and sharing best practices among entrepreneurs and innovators. These events offer an invaluable chance to engage with experts in the field, gain insights into effective practices, and become more familiar with the Lean Startup methodology.
Entrepreneurs and business leaders can foster connections with potential partners, mentors, and investors, thereby accelerating their growth and success, by attending Lean Startup conferences, meetups, and joining a lean startup circle. These events and communities also provide a supportive environment where participants can exchange ideas, ask questions, and learn from the experiences of others who have successfully applied Lean Startup principles.
Educational Programs
Educational programs, such as workshops and courses, teach Lean Startup principles and techniques to aspiring entrepreneurs and business leaders. These programs offer:
- Invaluable practical knowledge and skills
- Access to experienced guidance and mentorship
- The chance to build connections
- A supportive community
Entrepreneurs and business leaders can acquire crucial knowledge and abilities for the effective implementation of the Lean Startup methodology by participating in educational programs centered on this approach. Furthermore, they can access experienced advice and mentorship, network with like-minded individuals, and become part of a supportive community.
Tools and Techniques for Lean Startups
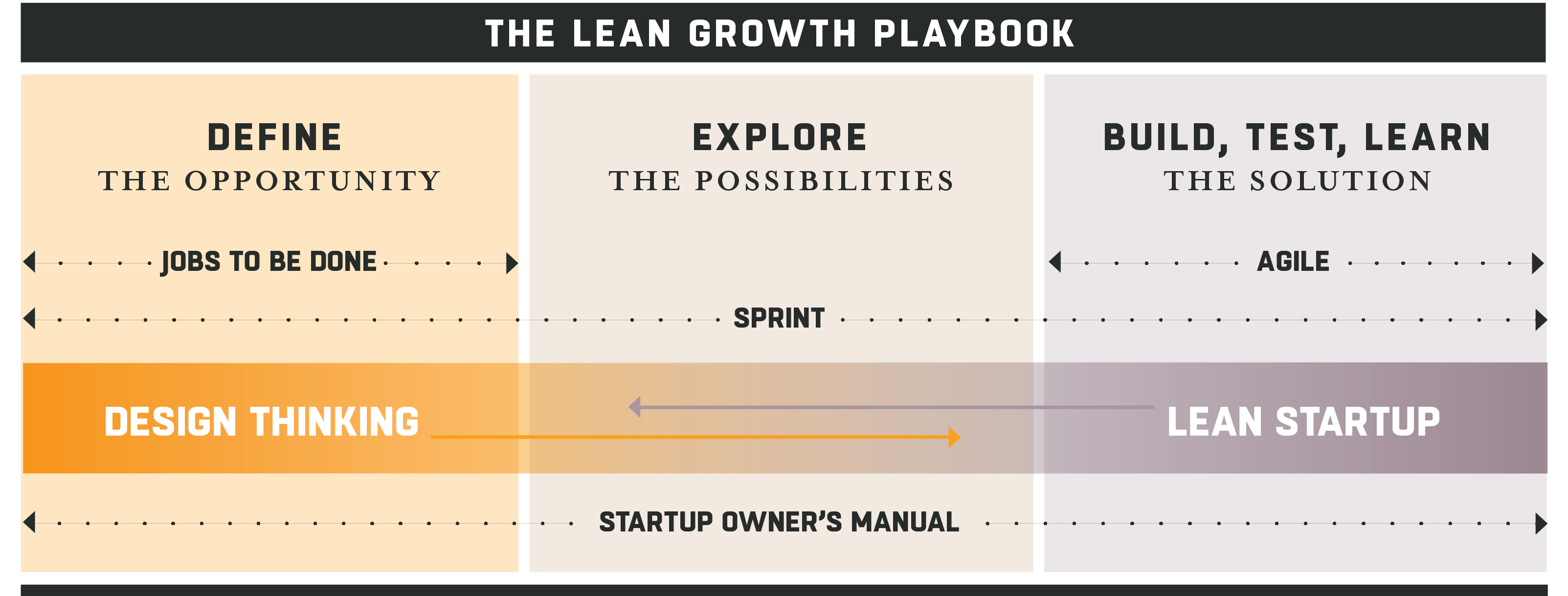
Tools and techniques available to Lean Startups include the Business Model Canvas, metrics, and analytics. These resources can help entrepreneurs test hypotheses, measure progress, and make data-driven decisions to improve their products and services.
Startups can continually iterate and refine their business models, leading to improved outcomes and heightened chances of success, by making use of tools and techniques found in the Startup Owner’s Manual.
In the following sections, we will explore the Business Model Canvas as a tool for developing and documenting business models, as well as the role of metrics and analytics in providing actionable insights for Lean Startups.
Business Model Canvas

As a potent visual tool, the Business Model Canvas assists startups in crafting and documenting their business models, formulating informed hypotheses, and making adjustments based on results derived from testing. The canvas includes nine parts:
- Customer segments
- Value propositions
- Channels
- Customer relationships
- Revenue streams
- Key resources
- Key activities
- Key partners
- Cost structure
Leveraging the Business Model Canvas enables startups to:
- Swiftly create and document their business models
- Formulate hypotheses
- Make adjustments based on test results
- Recognize potential areas for improvement
- Concentrate on the most significant aspects of the business
Metrics and Analytics
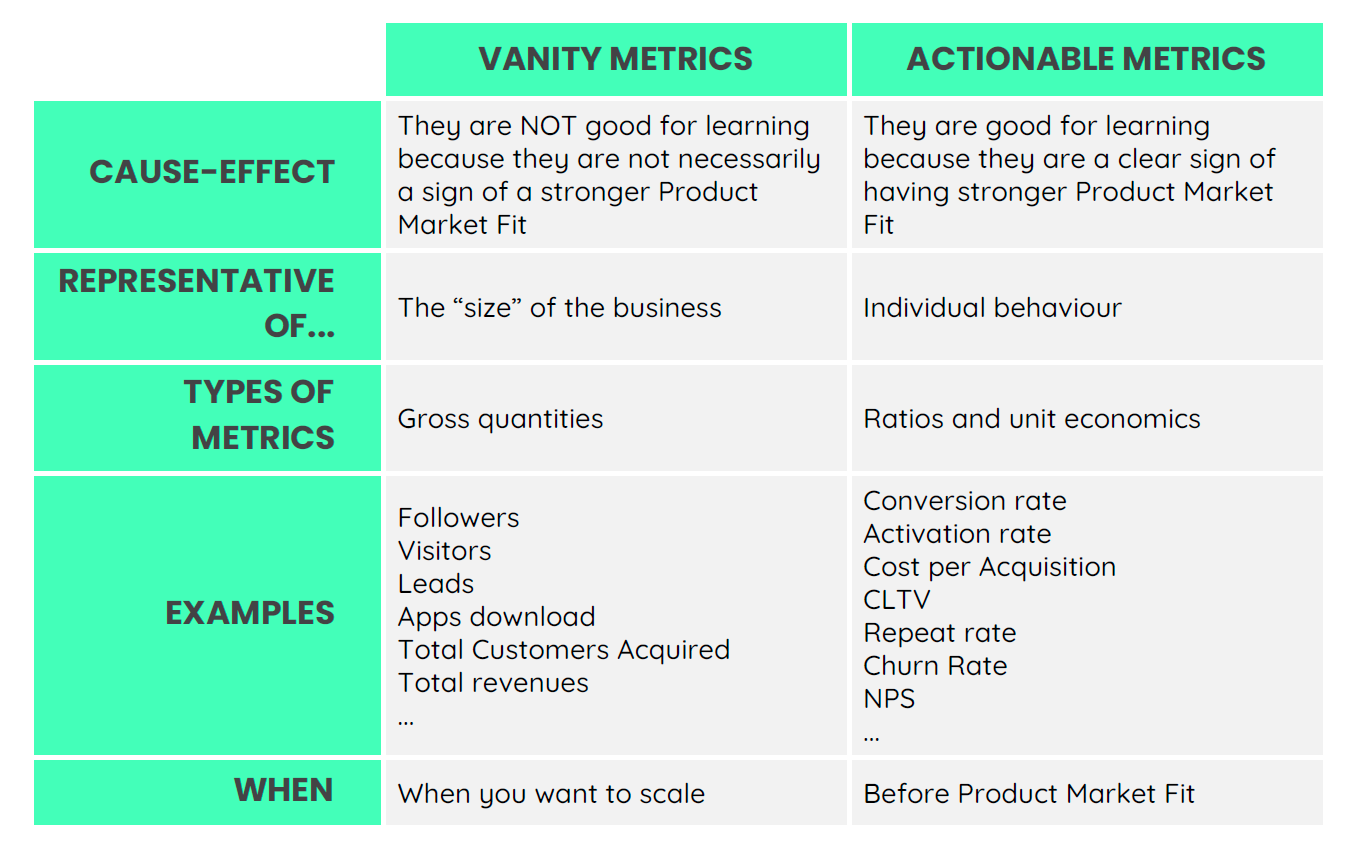
Metrics and analytics are essential to Lean Startups, offering valuable data to inform decisions and enable ongoing advancement. These tools can be utilized to validate hypotheses, measure progress, and pinpoint areas for improvement. Data-driven decision making can assist Lean Startups in making well-informed decisions and optimizing their processes.
Startups can glean insights into their customers’ needs, preferences, and behaviors, thus informing product development and marketing strategies, by making use of metrics and analytics. Furthermore, these tools can help startups track their progress and make adjustments based on real-time data, ensuring that they are continuously improving and adapting to the market.
Criticisms and Debates
Despite the widespread adoption and success of the Lean Startup methodology, its effectiveness and applicability in certain contexts have spurred criticisms and debates. Some critics argue that the approach overemphasizes cost-cutting, potentially hindering growth and innovation. Additionally, there are debates about the suitability of Lean Startup principles for certain sectors, such as healthcare, education, and government.
In the following sections, we will explore these criticisms and debates in more detail, discussing:
- The concerns surrounding cost-cutting
- The concerns surrounding industry-specific applicability
- Potential solutions and adaptations for these challenges.
Cost-Cutting Controversy
Some believe that the Lean Startup approach’s strong emphasis on cost-saving could potentially restrict expansion and creativity. Critics argue that focusing too much on “running lean” as a goal, rather than as a tool for staying afloat while competing in the market, can lead to negative consequences.
However, rather than primarily focusing on cost-cutting, the Lean Startup methodology emphasizes quickly and effectively reaching a viable product through iterative experimentation and uncertainty reduction, following the lean startup methodology principles. By focusing on these objectives, startups can strike a balance between cost-efficiency and innovation, ultimately leading to greater success.
Industry-Specific Concerns
The suitability of Lean Startup principles for certain sectors like healthcare, education, and government is a point of debate, considering the unique challenges and requirements these industries pose. Critics argue that the methodology may not be universally applicable, and that adaptations may be necessary for it to be effective in different contexts.
Despite these concerns, numerous organizations across different sectors have successfully embraced the Lean Startup methodology, yielding remarkable results. By adapting the principles to suit their specific needs, these organizations have been able to drive innovation, improve customer satisfaction, and stay competitive in their respective markets.
Summary
Our exploration of the Lean Startup methodology has taken us on a journey from its inception to its core principles, its triumphant success stories, and the wealth of resources available for both pioneering entrepreneurs and established corporations. While the methodology has its critics and sparks ongoing debates, its undeniable potency in propelling innovation, fostering growth, and steering success across a myriad of industries stands firm. As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of business, embracing the Lean Startup methodology could be the key to unlocking sustainable growth and innovation. It's not just a tool for startups, but a transformative approach that can infuse agility, customer-centricity, and continuous learning into any business's DNA.
So, let's keep moving, keep iterating, and keep innovating.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 principles of lean startup?
The Lean Startup model is based on five key principles: Entrepreneurs are everywhere, Entrepreneurship is management, Validated Learning, Innovation Accounting, and Build-Measure-Learn.
These allow startups to create, measure, and iterate quickly in order to develop a successful business model.
What are Lean Concepts and the Lean Startup Movement?
The lean startup movement is grounded in lean concepts, principles primarily derived from the manufacturing industry. Lean thinking focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing value, principles that have been adapted and applied to the startup context to remarkable effect.
At the heart of the lean startup approach is the idea of creating a scalable business model through rapid scientific experimentation, customer feedback, and iterative product releases. This approach contrasts sharply with the traditional method of investing heavily in a product before fully understanding the market demand.
How does the Lean Start up methodology improve business plans?
A key tool in the lean startup arsenal is the "business model canvas," a visual chart that allows entrepreneurs to map out key aspects of their business model. This tool facilitates a clear understanding of how different components of the business interact, from customer relationships and channels to revenue streams and key resources. This replaces elaborate business plans typically used in the business planning process.
The business model canvas is a powerful tool for "business model generation," the iterative process of refining and evolving a business model based on customer feedback and market response.
Why is customer feedback crucial to the lean startup method?
Central to the lean startup methodology is the concept of "customer discovery." Rather than investing time and resources into developing products or services based on assumptions about what the market wants, lean startups engage with potential customers early and often, using their feedback to guide the development process.
This focus on customer feedback helps startups avoid the pitfall of vanity metrics, those impressive-looking numbers that don't necessarily translate to sustainable growth or long-term success. Instead, lean startups measure actual progress through actionable metrics that reflect genuine customer interest and engagement.
How does lean methodology improve the innovation process?
Innovation processes in lean startups differ significantly from those in traditional businesses. Instead of following a linear path from idea to product, lean startups operate in a loop of building, measuring, and learning. This approach, often referred to as "agile development," allows for swift adaptation to market feedback and changing circumstances.
Lean startups also prioritize the development of "minimum viable products" (MVPs) — versions of a product with just enough features to satisfy early customers and provide feedback for future product development. This strategy allows startups to test their business hypotheses, shorten product development cycles, and pivot as necessary, all while minimizing risk and resource expenditure.
What is lean startup thinking?
Lean Startup is an approach to innovation that focuses on solving real user needs while eliminating waste and streamlining production. It is based on continuous feedback loops and encourages rapid iteration in order to better engage end users and identify the big picture associated with each progress phase.
This approach is designed to help entrepreneurs and innovators create successful products and services with minimal resources. It emphasizes the importance of testing and validating ideas quickly, and encourages experimentation and iteration in order to develop new ideas.
What is the Lean Startup methodology and why is it important?
The Lean Startup methodology focuses on reducing waste, maximizing value and leveraging customer feedback to create successful products, thus being essential for businesses to succeed in today’s competitive market.
How is the Lean Startup methodology different from traditional business practices?
The Lean Startup methodology encourages experimentation, customer-centricity, and fast iteration, in contrast to traditional business practices that prioritize extensive planning and forecasting.
Can established companies benefit from implementing Lean Startup practices?
Yes, established companies can benefit from Lean Startup practices to stay competitive and drive innovation.

